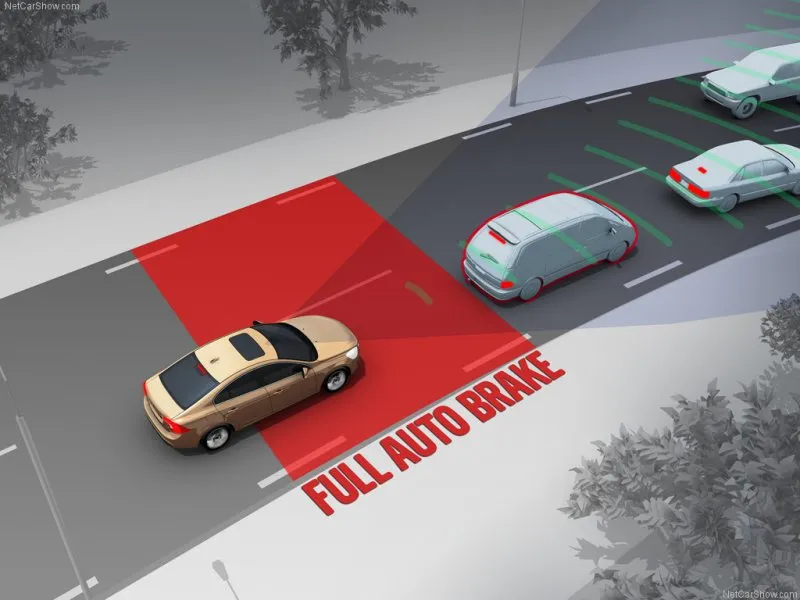
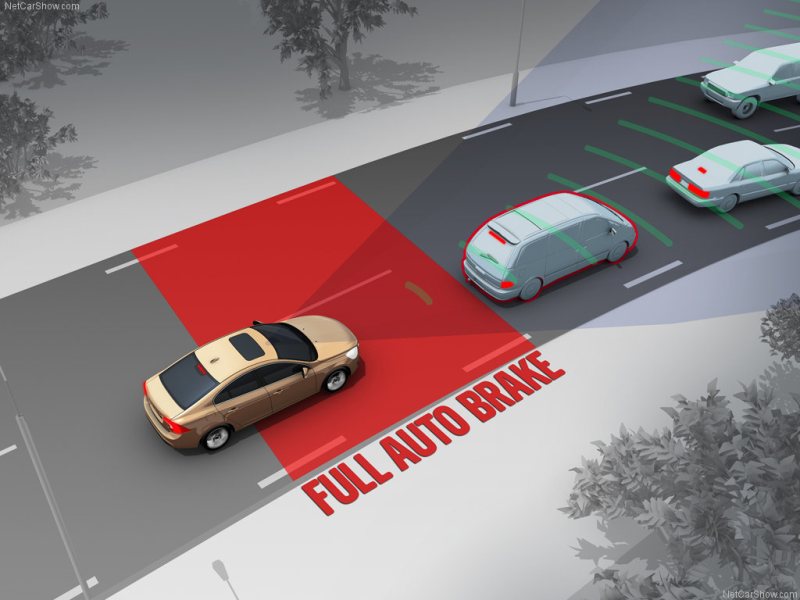
Imagine driving in the city during rush hour and your phone starts to ring. As you lose focus for a split second trying to answer the call, the car travelling in front of you suddenly slams on the brakes. In a situation like this, a crash-avoidance feature like a system that can automatically brake itself to avoid the crash can save you a lot of inconvenience, money and more importantly, possibly your life.
Whether you’re buying a new or used car, it’s very important that you spend some time and do some research to make sure that it’s safe for you and your occupants. Besides making sure that the seat belts and air bags are fitted as standard, we’ve listed out 10 prevalent active and passive safety features that you might want to look out for when buying a car, that could prevent you from possible mishap in the future.
1. Reverse camera. A valuable safety and convenient feature, reverse cameras not only gives drivers assurance when backing out of a parking spot or down a driveway, it is also very helpful in detecting objects that are hidden from your mirrors, especially small children and animals. Bigger cars like SUVs, have bigger blind spots and might hamper your view when reversing, so having one is not only more convenient, it’s also safer.
2. Electronic Stability Control (ESC) helps drivers to avoid crashes by reducing the danger of skidding, or losing control as a result of over/under-steering. ESC becomes active when a driver loses control of their car, or if the tyres lose traction. It uses computer controlled technology to apply individual brakes and help bring the car safely back on track, without the danger of the car skidding out of the lane. The importance of ESC has made this safety feature a mandatory fitment across Europe last year.
ESC has many different names depending on the make of the automaker, but they all operate in the same manner. They are also called Electronic Stability Program (ESP) Dynamic Stability Control (DSC), Active Stability Control (ASC) or Vehicle Stability Control (VSC). Check out the video of how it works below:
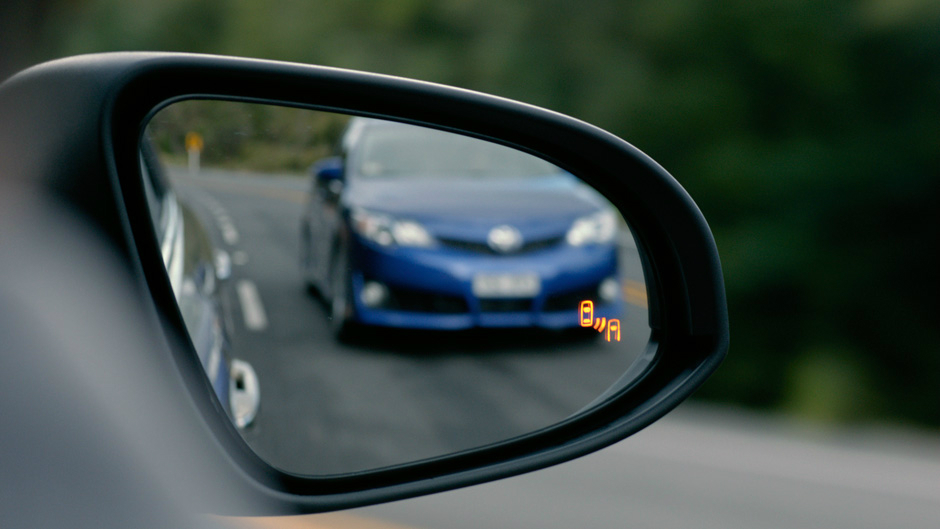
3. Blind spot assist makes motorway driving safer by helping to prevent accidents when you want to change lanes. The system monitors the areas to the left and right of the car, and warns you of a potentially hazardous situation by means of flashing warning lights in the exterior wing-mirrors. This safety feature is useful, especially on our local roads where you there’s always a motorist or motorcyclist creeping up behind you as you are changing lanes. Blind spot assist also has different names depending on the make of the automaker like Blind Spot Info System (BLIS) and Blind Spot Monitoring (BSM), Honda for instance, has a Lane Watch camera-type feature that will appear on the vehicle’s Display Audio screen to help decrease your passenger-side blind spot when changing lanes.
4. Emergency Brake assist. During an emergency stop, sometimes, the driver does not brake hard enough to come to a complete stop, so brake assist senses emergency braking by detecting the speed or force at which the driver presses the brake pedal and boosts the power as needed.
5. Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) prevents the wheels of a from vehicle locking-up as the brake pedal pressure is applied suddenly in an emergency or short stopping distance. This enables the driver to retain steering control, preventing skidding and loss of traction. ABS is particularly useful, especially when driving in rainy days. ( Point to note: ABS does NOT allow for shorter braking distances, this is a common misconception, it only allows the driver to maintain steering control during hard / emergency braking. ABS is not an excuse to tailgate, thinking you can stop in time. – CW)
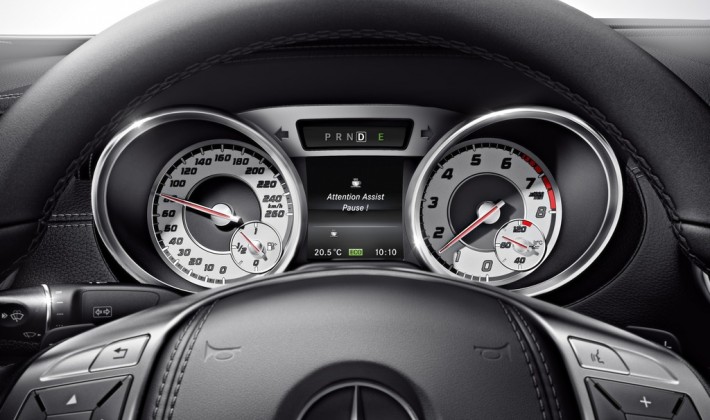
6. Attention Assist. Research indicates that as many as 30% of traffic accidents are related to drowsiness, and these are often the most catastrophic. Many automakers feature this system that use sensors to monitor driver attention and detect drowsiness alerting the driver to take a break. In Mercedes-Benz cars for example, the system announces it’s time to take a break with an audible warning and a visual message that includes a coffee-cup icon.
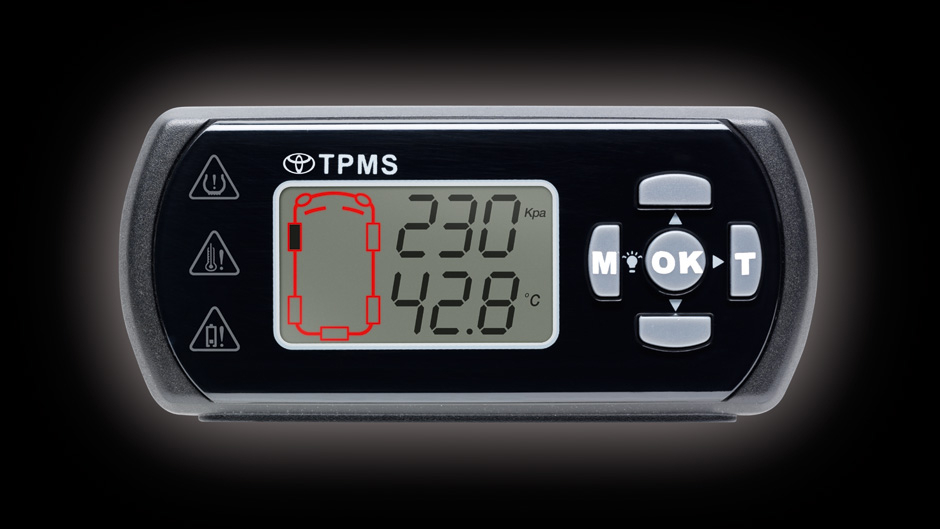
7. Tyre Pressure Monitoring (TPM). Tyres play a very important role in your car because there are many potential dangers of driving a car with deflated tyres, especially at high speeds. Sometimes, you won’t be able to notice a punctured tyre so TPM use sensors to alert the driver when tyre pressures drop below a designated PSi. TPMs are now a standard feature in many Toyota models.
8. City Safety. In reference to the situation mentioned earlier, City Safety prevents or reduces frontal collisions by using a sensor to monitor traffic in front of you. If it detects a risk of collision, it builds-up brake pressure so they respond instantly if you apply them. If you don’t, the car will automatically apply the brake when necessary. This system is normally active at speeds up to 50 km/h and are now available in many Volvo models.
9. Adaptive High Beam Assist. High beams normally provide extra vision for the driver, especially when driving at night, but you can hardly use it because you don’t want to blind oncoming drivers. Some automakers like Mercedes-Benz feature Adaptive High Beam Assist that have a specialized camera that will scan the road ahead for the lights being given-off by other vehicles. Based on the calculations that it receives, it will maximize its own illumination while ensuring that it doesn’t create an unwanted glare to oncoming vehicles. This is an essential safety feature that not only protects you but also other drivers on the road.
10. Traction Control System. When you are starting the vehicle or accelerating on a wet surface, you could lose control of the steering because of wheel spin. Traction Control will help prevent such events from happening by continually monitoring the traction between the tyres and the surface of the road. When it detects wheel spin, the system applies brakes or retards power from the engine to regulate spinning and help ensure proper contact of tyres. This helps prevent the car from becoming unstable, and also works while on the move.
Source: Mercedes-Benz, Volvo, Volkswagen, EuroNCAP, Toyota, Honda